Reading notes: Reasoning with latent structure refinement for document-level relation extraction
Published:
Reasoning with Latent Structure Refinement for Document-Level Relation Extraction
arxiv link of the source paper
1. Contributions of this paper:
1. Achieve better document-level RE/reseaoning results using a stronger graph which captures more non-local interactions. The model is called LSR(Latent Structure Refinement) model
2. This graph is treated as a latent variable, automatically induced with a refinement strategy which incrementally aggregate relevant information.
3. Example of how the model can do step-by-step “relational reasoning”:
- Lutsenko is a former minister of internal affairs.
- He occupied this post in the cabinets of Yulia Tymoshenko.
- The ministry of internal affairs is the Ukranian police authority. The question is what is the relation between “Yulia Tymoshenko” and “Ukranian”. When reading the 3 sentecnes, the model will know:
- Lutsenko and “He” are mentions of same entity
- Lutsenko works with Tymenshenko
- Lutsenko managed internal affairs, which is a Ukranian authority
- Thus, Lutsenko is Ukranian -> Tymenshenko has nationality of Ukranian
2. Limitations of current practices?
1. Mostly with-in sentences, ignoring the rich information accross sentences:
- This is because most of the current graph (even document-level) model dependencies based on (1)syntactic trees(POS), (2)coreference, or (3)heuristics
- Do not have “relational reasoning”
3. About LSR model
1. What are the major subtasks?:
- Node constructor
- (1)encode sentences with contextual representation
- (2)construct representations of 3 types of nodes: mention, entity, and MDP(meta dependency paths)
- What is MDP nodes?
- In each sentences, there are multiple dependency path. The shortest parths are MDP path. The nodes in MDP paths are MDP nodes.
- Dynamic reasoner
- First, it induce a doc-level structure using extracted nodes
- Second, it keeps updateing node representations based on information propagatoin(iteratively refined)
- Classifier
- Given the final node representations after refinement, calculate classification scores
2. Choice of actual model components?
- Context enoder: BiLSTM or BERT
3. Steps
- Context encoding
- Given a doc d, for sentence di, its j-th word has hidden state hij = [
;
], which is the concatenation of hidden states of two directions.
= LSTM(
,
), where
is the word embedding of the j-th token.
- Similarly,
= LSTM(
,
)
- In this way, the mention nodes and MDP nodes will be represented. For entity nodes, it will be constructed by averaging the related coreference mention nodes.
- Given a doc d, for sentence di, its j-th word has hidden state hij = [
- Node extraction
- Use tokens on shortest dependency path between mentions in sentence. It will effectively make use of relevant information while ignoring the irrelevant one.
- Structure induction
- Induce latent dependency structure using structured attention and a variant of Kirchhoff’s Matrix-Tree Theorem
- Given the representation of the i-th and j-th nodes to be ui and uj, calculate the pair-wise unnormalized attention scores sij between them. sij = (tanh(Wpui))TWb(tanh(Wcuj))
- Compute root score which is the unnormalized probability of the i-th node to be selected as the root node of the structure sri = Wrui
- Calculate marginal probability of each dependency edges
- Multi-hop reasoning
- Use GNN, more specifically GCN(convolutional).
- A graph G with n nodes can be represented as an n x n adjacency matrix A, which induced by previous structure induction
- A node i at level l will have representation uli, which can be computed using ul-1i
- Formula: 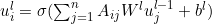
- Iterative refinement
- Will do refinement of structure N times, by stacking N blocks of the dynamic reasoners.
- The induced structure will be more and more refine as more and more information aggregated
- Classifier
- After N times refinements, we will get final representations of all nodes. We will compute the probability of these two entities belong to a certain relation r using a bilinear function.
Formula: 


